王鹏瑞1,2, 杨 丹1, 张 雪1, 李 静1, 闫良国1
(1. 济南大学 水利与环境学院, 山东 济南 250022;2. 济南市市中区环境监测站, 山东 济南 250001)
DOI:10.13732/j.issn.1008-5548.2021.03.008
收稿日期: 2020-12-27,修回日期:2021-02-22,在线出版时间:2021-04-07 11:27。
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目,编号:21577048。
第一作者简介:王鹏瑞(1990—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境监测与水污染治理技术。E-mail:502276827@qq.com。
通信作者简介:闫良国(1971—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为环境功能材料。E-mail:chm_yanlg@ujn.edu.cn。
摘要:为寻找高效吸附水中六价铬(Cr(Ⅵ))的水滑石功能材料,以水热法制备钙铝(CaAl-LDH)和铁铝水滑石(FeAlLDH) 2种吸附剂,通过X射线衍射仪、红外光谱仪、扫描电镜和比表面积测定仪研究其结构和性质,采用批次平衡实验比较研究其对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能。结果表明:CaAl-LDH和FeAl-LDH具有水滑石的特征衍射峰和介孔结构,呈六边形片状,比表面积分别为8.746、159.5 m2/g; 2种材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附速率较快,在30 min达到平衡,且吸附过程不受溶液pH值的影响,溶液中存在的常见阴离子对Cr(Ⅵ)影响较小;吸附动力学和等温线数据分别符合拟二级动力学方程和Langmuir等温线模型,CaAl-LDH和FeAl-LDH对Cr(Ⅵ)的最大吸附量分别为34.92、51.31 g/kg。
关键词:钙铝水滑石;铁铝水滑石;六价铬;吸附;水热法
Abstract:To obtain layered double hydroxide( LDH) based functional materials for efficient removal hexavalent chromium( Cr( Ⅵ)) from water,CaAl-LDH and FeAl-LDH were prepared by the hydrothermal method. The structure and property were investigated by X-ray diffraction pattern( XRD),Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,scanning electron microscopy and specific surface area measurement. Batch equilibrium experiments were used to evaluate the adsorption performance of the as-prepared CaAl-LDH and FeAl-LDH for aqueous Cr( Ⅵ). The experimental results show that CaAl-LDH and FeAl-LDH have typical XRD peaks of LDH,mesoporous structure and hexagonal laminar shape. The specific surface areas are 8. 746 and 159. 5 m2/g. The adsorption processes of Cr( Ⅵ) by CaAl-LDH and FeAl-LDH are fast and reache equilibrium within 30 min,andare not affected by the initial solution pH value and the common coexisting anions. The kinetic and isothermal data follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation and the Langmuir model,respectively. The maximum adsorption capacities of CaAl-LDH and FeAl-LDH for aqueous Cr( Ⅵ) are 34. 92 and 51. 31 g/kg.
Keywords:CaAl-LDH; FeAl-LDH; hexavalent chromium; adsorption; hydrothermal method
参考文献(References):
[1]张爽, 丁欣欣, 闫良国. 改性水滑石类材料的制备及其吸附性能研究进展[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2021, 27(1): 1-10.
[2]TRAN H N, NGUYEN D T, LE G T, et al. Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium onto layered double hydroxides-based adsorbents: a systematic in-depth review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 373: 258-270.
[3]JOSE N A, ZENG H C, LAPKIN A A. Hydrodynamic assembly of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanostructures[J]. Nature Communication, 2018, 9(1): 4913-4917.
[4]ZUBAIR M, DAUD M, MCKAY G, et al. Recent progress in layered double hydroxides (LDH)-containing hybrids as adsorbents for water remediation[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 143: 279-292.
[5]GUPTA K, HUO J B, YANG J C, et al. (MoS4)2- intercalated CAMoS4·LDH material for the efficient and facile sequestration of antibiotics from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 355: 637-649.
[6]ASIABI H, YAMINI Y, SHAMSAYEI M, et al. Highly selective and efficient removal and extraction of heavy metals by layered double hydroxides intercalated with the diphenylamine-4-sulfonate: a comparative study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 323: 212-223.
[7]YU S J, WANG X X, CHEN Z S, et al. Layered double hydroxide intercalated with aromatic acid anions for the efficient capture of aniline from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 321: 111-120.
[8]CHEN H, LIN J H, ZHANG N, et al. Preparation of MgAl-EDTA-LDH based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorption properties of copper(II) from wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 345: 1-9.
[9]ZHANG L, FU F L, TANG B. Adsorption and redox conversion behaviors of Cr(VI) on goethite/carbon microspheres and akaganeite/carbon microspheres composites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 151-160.
[10]RAJAPAKSHA A U, VITHANAG M, OK Y S, et al. Cr(VI) Formation related to Cr(III)-muscovite and birnessite interactions in ultramafic environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(17): 9722-9729.
[11]张帆, 李菁, 谭建华, 等. 吸附法处理重金属废水的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 11: 220-227.
[12]苏欣悦, 丁欣欣, 闫良国. 改性水Fe3O4磁性纳米材料的制备及水处理应用进展[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2020, 26(6): 1-10.
[13]LU Y, JIANG B, FANG L, et al. High performance NiFe layered double hydroxide for methyl orange dye and Cr(VI) adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152: 415-422.
[14]LI J, YAN L G, YANG Y T, et al. Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of aqueous hexavalent chromium by EDTA intercalated layered double hydroxides: XRD, FTIR, XPS, and zeta potential studies[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43: 15915-15923.
[15]GORE C T, OMWOMA S, CHEN W, et al. Interweaved LDH/PAN nanocomposite films: application in the design of effective hexavalent chromium adsorption technology[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 794-801.
[16]CHEN S X, HUANG Y F, HAN X X, et al. Simultaneous and efficient removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange on LDHs decorated porous carbons[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 352: 306-315.
[17]OGATA F, UETA E, KAWASAKI N. Characteristics of a novel adsorbent Fe-Mg-type hydrotalcite and its adsorption capability of As(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 59: 56-63.
[18]YUE X Y, LIU W Z, CHEN Z L, et al. Simultaneous removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) by Mg-Al-Cl layered double hydroxide and mechanism insight[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 53: 16-26.
[19]HE X, QIU XH, CHEN JY. Preparation of Fe(II)-Al layered double hydroxides: application to the adsorption/reduction of chromium[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 516: 362-374.
[20]贾云生, 王火焰, 赵雪松, 等. CaAl类水滑石的磷酸根吸附性能及其影响因素研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(11): 1207-1213.
[21]SHAN R R, YAN L G, YANG K, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4/MgAl-LDH composite for effective removal of three red dyes from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 252: 38-46.
[22]WANG X X, YU S Q, WU Y H, et al. The synergistic elimination of uranium (VI) species from aqueous solution using bi-functional nanocomposite of carbon sphere and layered double hydroxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 342: 321-330.
[23]PEREZ M R, PAVLOVIC I, BARRIGA C, et al. Uptake of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ on Zn-Al layered double hydroxide intercalated with EDTA[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2006, 32(3/4): 245-251
[24]LU Y, JIANG B, FANG L, et al. High performance NiFe layered double hydroxide for methyl orange dye and Cr(VI) adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152: 415-422.
[25]LI J, FAN Q H, WU Y J, et al. Magnetic polydopamine decorated with Mg-Al LDH nanoflakes as a novel bio-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of potentially toxic metals and anionic dyes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(5): 1737-1746.
[26]ZHU K R, GAO Y, TAN X L, et al. Polyaniline-modified Mg/Al layered double hydroxide composites and their application in efficient removal of Cr(VI)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(8): 4361-4369.
[27]DENG L, ZENG H X, SHI Z, et al. Sodium dodecyl sulfate intercalated and acrylamide anchored layered double hydroxides: a multifunctional adsorbent for highly efficient removal of Congo red[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 521: 172-182.
[28]林巧莺, 陈岳民. 碳酸根型镁铝水滑石对铬酸根和磷酸根离子的吸附性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9: 4687-4696.
[29]LI L, QI G X, WANG B D, et al. Fulvic acid anchored layered double hydroxides: a multifunctional composite adsorbent for the removal of anionic dye and toxic metal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 343: 19-28.
[30]LI B, ZHANG Y X, ZHOU X H, et al. Different dye removal mechanisms between monodispersed and uniform hexagonal thin plate-like
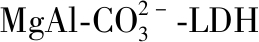 and its calcined product in efficient removal of Congo red from water[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 673: 265-271.
and its calcined product in efficient removal of Congo red from water[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 673: 265-271.
[31]MIRETZKY P, CIRELLI A F. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 180(1/2/3): 1-19.
[32]CUI L M, WANG Y G, GAO L, et al. EDTA functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for removal of Pb(II), Hg(II) and Cu(II) in water treatment: adsorption mechanism and separation property[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 281: 1-10.
[33]WANG X X, YU S Q, WU Y H, et al. The synergistic elimination of uranium (VI) species from aqueous solution using bi-functional nanocomposite of carbon sphere and layered double hydroxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 342: 321-330.
[34]LU Y, JIANG B, FANG L, et al. High performance NiFe-layered double hydroxide for methyl orange dye and Cr(VI) adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152: 415-422.
[35]YAN L, YANG K, SHAN R, et al. Calcined ZnAl- and Fe3O4/ZnAl-layered double hydroxides for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(117): 96495-96503.
[36]DAS N N, KONAR J, MOHANTA M K, et al. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Se(IV) from their aqueous solutions onto Zr4+-substituted ZnAl/MgAl-layered double hydroxides: effect of Zr4+ substitution in the layer[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 270: 1-8.
[37]GUO X X, ZHANG F Z, PENG Q, et al. Layered double hydroxide/eggshell membrane: an inorganic biocomposite membrane as an efficient adsorbent for Cr(VI) removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166: 81-87.

